PADsynth algorithm
1) Introduction
2) Sound examples of instruments that use this algorithm (using ZynAddSubFX)
3) Description of the algorithm
3.1) General descripton (diagrams,etc..)
3.2) Steps of the algorithm (with pseudocode)
3.3) Public domain C/C++ code that shows some simple implementations
3.4) Public domain C++ class that implements the algorithm (ready to use)
4) Tips and suggestions
5) Conclusions
1) Introduction
This algorithm
generates very beautiful sounds, even if its idea is much simpler than
other algorithms. It generates a perfectly looped wavetable sample which
can be used in instruments. It easily generates sounds of ensembles,
choirs, metalic sounds (bells) and many other types of sound.
I want to make this algorithm known and you are
welcome to learn and use this algorithm into your projects or products
(non-commercial or commercial). You will not be dissapoined by this
algorithm. This page includes some public domain C/C++ sources that can
be used in your projects/products.
This algorithm is implemented in
ZynAddSubFX in the
PADsynth module and you can download it to hear yourself how beautiful
sounds it can generate. Before reading this document, I recomand to listen
to all sound examples in the next category. It will give you an idea of what
kind of sounds it produces.
2) Sound examples of instruments that use this algorithm
These sound examples are generated by ZynAddSubFX.
All instruments's wavetables are generated by this algorithm.
These examples are grouped into 2 categories:
2.1) With FX. In this category, some effects are
used. This effects can be reverberation, phaser, etc. Mostly, the only
effect was the reverberation.
2.2) Without FX. All instruments in this category
the instruments are "dry". No reverberation, no other effects.
Parameter files of above examples (for ZynAddSubFX).
3) Description of the algorithm
In order to understand how this algorithm works, you
need to be familiar with how I think about the musical instruments. Please read an introduction for the description of the meaning and the importance of Bandwidth of each harmonic and Randomness.
3.1) General description
This algorithm generates some large wavetables that
can played at diferent speeds to get the desired sound. This algorithm
describes only how these wavetables are generated. The result is a
perfectly looped wavetable. Unlike other synthesis methods which use
Inverse Fast Fourier Transform, this one does not use overlap/add methods and there is only one IFFT for the whole sample.
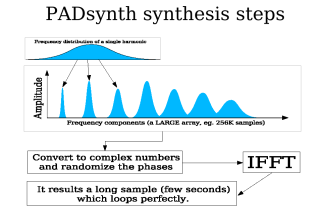
The basic steps are:
- Make a very large array that represents the amplitude spectrum of the sound (default all values are zero)
- Generates the distribution of each harmonic in frequency and add it to the array
- Put random phases to each frequency of the spectrum
- Do a single Inverse Fourier Transform of the whole spectrum. Here is no
need of any overlapping windows, because there is only one single IFFT
for the whole sample.
The ouput is the sample which can
be used as a wavetable. In the next image, the steps are represented
graphically:
3.1.1) The bandwidth of each harmonic
I consider one harmonic(overtone)
as being composed of many frequencies. These sine components of one
harmonic are spread over a certain band of frequencies.
Higher harmonics has bigger
bandwidth. In natural choirs/ensembles the bandwidth is proportional to
the harmonic's frequency.
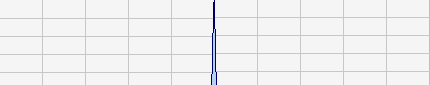
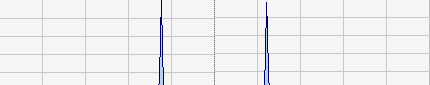
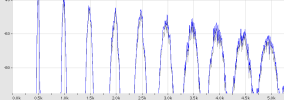
Here is an example of a spectrum of an instrument generated by ZynAddSubFX:
 |
 |
| full spectrum |
closeup of the spectrum |
The harmonics becomes wider and
wider, until at a certain frequency, where they may merge to a noise band
(as in the full spectrum image from above). This is a normal thing and I
recomand to not avoid this by limiting the bandwidth of the harmonics.
3.1.2) The frequency distribution of one harmonic/overtone (or the harmonic profile)
This describes the function of the spread of the harmonic.
Here are some examples of how they can be spread:
a) A special case is where there
is only a single sine component inside the hamonic. In this case, the
harmonic and the "sine component" are the same thing.
Audio example:
single harmonic,
many harmonics
d) Normal (Gaussian)
distribution. The sine components amplitude are bell shaped. The
largest amplitude is in the center of the band. This distribution gives
the most natural sounds (it simulates a very, very large enssemble).
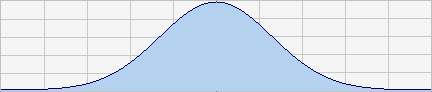
Audio example:
single harmonic,
many harmonics
Of course, you can use many
others harmonic's profiles. ZynAddSubFX's PADsynth module offers many
ways to generate the harmonic profile.
Also, it's very important that the
harmonic must have the same amplitude, regardless of the profile functions/parameters
and the bandwidth.
3.1.3) The phases of the sine components of the harmonics
This algorithm considers the phases of the sine components of each harmonics as random.
3.2) Steps, input and output of the algorithm (with pseudocode)
3.2.1) Steps of the basic algorithm
Input:
N - wavetable size. It's recomanded to be a
power of 2. This is, usually, a big number (like 262144)
samplerate - the samplerate (eg. 44100)
f - frequency of the the fundamental note (eg. 440)
bw - bandwidth of first harmonic in cents (eg. 50 cents); must be greater than zero
number_harmonics - the number of harmonics. Of course, number_harmonics<(samplerate/f)
A[1..number_harmonics] - amplitude of the harmonics
Output:
smp[0..N-1] - the generated wavetable
Internal variables:
freq_amp[0..N/2-1] = {0,0,0,0,...,0}
freq_phase[0..N/2-1], etc...
Functions:
RND() returns a random value between 0 and 1
IFFT() is the inverse fourier transform
normalize_sample() normalizes samples
profile(fi,bwi){
x=fi/bwi;
return exp(-x*x)/bwi;
};
Steps:
FOR nh = 1 to number_harmonics
bw_Hz=(pow(2,bw/1200)-1.0)*f*nh;
bwi=bw_Hz/(2.0*samplerate);
fi=f*nh/samplerate;
FOR i=0 to N/2-1
hprofile=profile((i/N)-fi,bwi);
freq_amp[i]=freq_amp[i]+hprofile*A[nh];
ENDFOR
ENDFOR
FOR i=0 to N/2-1
freq_phase[i]=RND()*2*PI;
ENDFOR
smp=IFFT(N,freq_amp,freq_phase);
normalize_sample(N,smp);
OUTPUT smp
3.2.2) The extended algorithm
The differences between the extended algorithm and the basic algorithm are minor:
There is an additional parameter:
bwscale:
that specify how much the bandwidth of the harmonic increase according
to it's frequency. Also, there is defined a function called relF(N) who
returns the relative frequency of the N'th overtone. It allows to
generate detuned harmonics or even metallic sounds (like bells).
The difference between the basic algorithm is at the computation of bw_Hz and fi:
bw_Hz=(pow(2.0,bw/1200.0)-1.0)*f*pow(relF(nh),bwscale);
fi=f*relF(nh)/samplerate;
If the relF(N) function returns N and the bwscale is equal to 1, this algorithm will be equivalent to the basic algorithm.
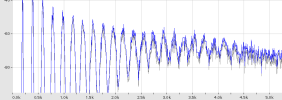
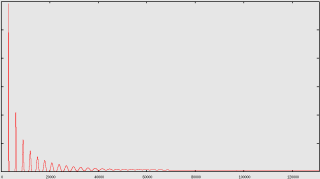
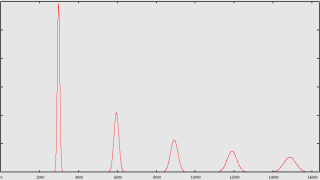
3.2.3) Example Graph of freq_amp array:
Graphs of the (basic algorithm) freq_amp array for
N=262144, f=500 Hz, bw=100 cents, samplerate=44.1 Khz, and A[] where
A[n]=1.0/sqrt(n)
 |
 |
| Graph of the full array |
Closeup of the graph of the array |
3.2.4) Example of the output of this algorithm (c_basic implementation)
c_basic_sample.ogg - this is the resulting smp array converted to ogg vorbis.
3.3) Public domain C/C++ code that shows a simple implementation
I wrote some C/C++ implementations of the basic algorithm and the extended algorithm.
The "c_basic" directory contains the basic
algorithm, "c_extended" contains the extended algorithm and the
"c_simple_choir" is the implementation of the basic algorithm to make a
simple choir.
These implementations are wrote to be
easy to understood and they are not optimised for speed. You can test
on Linux by running the ./compile.sh scripts. It's recomanded to
have snd installed, to make possible to hear the results as wav file.
Of course, you can import the results into your instruments, because
the waves are perfectly looped (set the first loop point to 0 and the
second to the end of the wav).
I put the source code under public domain, but it
depends on FFTW3 library, so, if you want to use into your products, you
must use your IFFT routines to avoid licensing issues of the FFTW library.
3.4) Public domain C++ class that implements the algorithm (ready to use)
To be easy to use this algorithm into your projects
or products, I made a ready-to-use C++ class. Only thing that you have
to do, is to provide it an IFFT routine. Please read the header file for details.
4) Tips and suggestions
- Keep in mind that the resulting wavetables are perfectly looped
- When using the wavetables into instruments, on each NoteOn, start from a random position and not
from the start. This avoids hearing the same sound on each keystroke
- You can use the same wavetable for generating stereo sounds, by playing
the same wavetable at different positions for left and right. The best
is to make the difference between left right as N/2
- Generate different wavetables for different pitches and use the one who is closest to the desired pitch
- Upsample or downsample the harmonics's amplitude array before running the algorithm, according to the fundamental frequency. In this case we need to set a parameter "base_frequency" which represents the frequency where the array is left unchanged.
Example: we have A_orig[]={1,2,1,3,0,0,1,0} and base_frequency is equal to 440 Hz
Here are some cases:
- A[] for 440 Hz: is the same as A_orig[]
- A[] for 220 Hz: is the A_orig[] upsampled by factor of 2
so: A[]={1, 1, 1.5, 2, 1.5, 1, 2, 3, 1.5, 0, 0, 0, 0.5, 1, 0.5, 0}
(the original A_orig amplitudes are shown as bold)
- A[] for 880 Hz: the A_orig[] is downsampled by a factor of 2
so: A[]={1.5, 2, 0, 0.5}
- A[] for F Hz: the A_orig[] is scaled by a factor of 440/F.
Even if this ideea is very simple, the resulting sounds are very
natural, because it keeps the spectrum constant according to the
harmonic's frequency and not to harmonic's number. This folows the
point 4 from the document where I described some principles regarding synthesis.
5) Conclusions
I hope that this algorithm will be implemented in
many software/hardware synthesizers. Use it, spread it, write about it, make beautiful instruments with it. If your synthesizer uses plenty of
samples, you can use this algorithm to generate many ready-to-use
samples.
This algorithm, this page, the images,
the implementations from this page, the audio examples, the parameter
files from this page
are released under Public Domain by Nasca Octavian Paul.
e-mail: zynaddsubfx AT yahoo DOT com